What does carbon negative mean?
 Copyright: Ministry of the Environment of Japan
Copyright: Ministry of the Environment of Japan
Carbon negative means the absorption of greenhouse gases exceeds its emission. The concept of carbon negative has gained attention in recent years as global warming has become a more critical and growing concern.
The IPCC report indicates more than two-thirds of the world’s greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a significant factor causing global warming. Therefore, global efforts to reduce CO2 emissions from current economic activities is an effective measure to mitigate global warming.
How to better control CO2 emissions would be the key to reducing greenhouse gases effectively.
Which is correct, carbon negative or positive?
While carbon negative and carbon positive share the same meaning, their focus is different.
Carbon negative focuses on emission with the goal of removing CO2 (being negative), while carbon positive focuses on absorption (being positive).
In essence, carbon positive implies that the amount of absorption exceeds the amount of emission amount (absorption – emission > 0), similar to the meaning of carbon negative.
Difference between carbon neutral, net-zero and carbon negative
“Carbon Neutral” is a term combining “carbon” and “neutral,” referring to a state where CO2 emissions and absorption are offsetting each other. Similarly, “Net-Zero emission” means that greenhouse gas emissions are effectively zero, and it is used almost synonymously with Carbon Neutral.
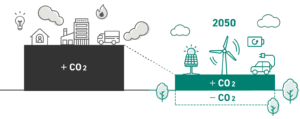
On the other hand, “Carbon Negative” describes a situation where the amount of absorbed CO2 exceeds its emitted ones, indicating a more advanced state of decarbonization than carbon neutrality.
In terms of aiming for CO2 emission reduction, Carbon Negative, Carbon Neutral, Net-Zero emissions and Carbon Positive all share the same direction or goal.
Benefits to be carbon negative for business
Carbon neutral is a prerequisite for achieving carbon negative, or CO2 absorption exceeding emissions.
While achieving carbon negative is more challenging than carbon neutral at the national level, it should be feasible at the entity level, i.e., company or industry, using negative emission technologies.
Promoting initiatives towards a decarbonized society
The focus on carbon negativity arose from the issue of global warming. According to the Sixth Assessment Report published in 2021 by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), if greenhouse gas emissions continue at a moderate level, the increase in temperature by 2100 is expected to be between 2.1 to 3.5°C. If emissions remain very high, the increase could be as much as 5.7°C.
If initiatives towards carbon negativity become widespread, not only will efforts to ‘reduce emissions’ be enhanced, but also efforts to ‘increase absorption’ will be further activated. This will provide a stronger impetus towards achieving a decarbonized society.
Showing off the Environmental Awareness
Global warming is one of the challenges facing society, and there is significant interest in how various companies are addressing this issue these days.
Additionally, this approach is likely to be a positive influence in the increasingly important area of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investments.
Current situation of carbon negative on the Earth

In order to tackle climate change, not only reducing CO2 emissions, but also removing the most abundant CO2 from the atmosphere are required.
WMO has announced that the average annual atmospheric CO2 concentration reached 417.9 ppm in 2022 and is expected to continue rising.
The adverse effects of global temperature rise, evidenced by extreme weather events and sea level rise, are escalating. According to NASA, the average global temperature increase was around 0.8°C in the 20th century and it has been increasing every year.
Therefore, reducing emission is a necessary action to mitigate global warming, and the carbon neutral and carbon negative initiatives are imperative in this context.
Technologies and practical examples of carbon negative solutions
Afforestation and blue carbon
Plant based technologies such as afforestation and blue carbon effectively increase the amount of CO2 absorbed. Research is underway to improve the absorption efficiency of mangrove forests and seaweed in a specific location.
Related Article:
What is the Blue Carbon? The importance of its system, and pros and cons
Afforestation and reforestation
Planting and restoring forests are a low-cost, energy-efficient approach with significant environmental benefits. Advanced technologies such as breeding elite trees that grow 1.5 times faster than traditional varieties and optimizing seedling production through soilless rooting will improve the CO2 absorption efficiency in reforested areas.
Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS)
BECCS is a technology that integrates biomass power generation with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. CCS involves capturing CO2 emissions from the atmosphere, power generation, or industrial processes, and then transporting them for storage deep underground. BECCS, not only producing energy but also reducing atmospheric CO2, is a key component of a sustainable energy strategy.
Carbon negative is a crucial concept in addressing climate change and it is essential to deepen the understanding of the concept to achieve this goal. Technical approaches such as afforestation, reforestation and BECCS play a critical role. As the world makes various efforts to challenge global warming, carbon negative initiatives should become an essential part of a sustainable future.
You May Also Interested in:
What dose carbon budget mean and how it help us to achieve net zero emissions?



Comments