What Is The Voluntary Carbon Market? Explaining Benefits And Challenges
- CO2-reduction

Table of Contents
- 1 What is the Voluntary Carbon Market?
- 2 Types of credits in the voluntary carbon markets
- 3 What are the differences between the voluntary and mandatory carbon markets?
- 4 What are the benefits of voluntary credits?
- 5 What are the challenges of voluntary credits?
- 6 How can voluntary credits be used effectively?
What is the Voluntary Carbon Market?
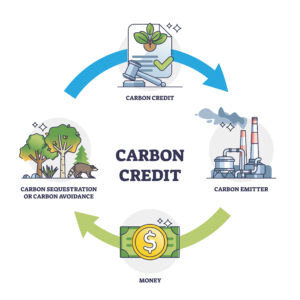
A voluntary credit is gaining attention because they can offset the CO2 emissions that are difficult to achieve through the managed phase out of fossil fuels or the introduction of renewable energy alone. The voluntary carbon markets are used to buy and sell different voluntary credits.
Types of credits in the voluntary carbon markets
There are several examples of voluntary credits sponsored by companies and private organizations. The following are the types of voluntary credits introduced by companies.
VCS (Verified Carbon Standard)
Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) is the world’s most widely traded voluntary credit. It was created in 2005 by an organization that includes private companies such as the International Emissions Trading Association and the World Business Council to certify voluntary credits, and is currently developed and managed by Verra.
There are many ways to generate credits, and among them are 15 types that are recognized but not limited to: energy, industrial processes, construction, transportation, waste, industry, agriculture, forests, grasslands, wetlands, livestock, livestock and manure. Credits can be generated through a variety of approaches and can be purchased.
Source: The VCS Project Cycle: Step by Step
GS (Gold Standard)
Gold Standard is a certification standard established in 2003 by environmental NGOs such as the World Wide Fund for Nature to guarantee the “quality” of projects. Not every project necessarily contributes to greenhouse gas reduction or sustainable development..
Therefore, GS standards are designed to help projects generate their own environmental benefits, which in turn allows buyers to purchase high quality credits.
ACR (American Carbon Registry)
Founded in 1996 by the nonprofit Winrock International, American Carbon Registry(ACR) is the world’s first private greenhouse gas registry.
Participating companies also utilize ACR-certified credits under the emissions trading system in California, USA.
CAR (Climate Action Reserve)
Climate Action Reserve(CAR) is a registry created by the State of California in 2001 for supporting voluntary calculation and public reporting of emissions to combat climate change. Its goal is to establish standards to improve the quality of carbon offset projects, issue high-quality credits, and build confidence in the global carbon market.
What are the differences between the voluntary and mandatory carbon markets?
In the voluntary carbon markets, companies and individuals voluntarily purchase carbon credits to offset their greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, the mandatory market is regulated by governments or international regulatory bodies to meet emission reduction targets. The key difference is whether the offset is mandatory or voluntary.
Types of carbon credits
In the voluntary carbon market, credits can come from a variety of projects, such as renewable energy, reforestation, and community projects. In contrast, credits in the mandatory market are based on specific regulatory frameworks, and the types of eligible projects are often more limited.
These differences mean that the two markets have different roles and functions in addressing climate change and managing carbon emissions.
| Voluntary Carbon Market | Mandatory Carbon Market | |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Entities buy credits to offset emissions voluntarily, often for sustainability or CSR goals. | Entities are legally required to limit or compensate for their emissions. |
| Participation | Optional, based on entity’s choice. | Required by law. |
| Carbon Credits | Represent voluntary emission reductions from projects like reforestation, renewable energy. | Issued as part of a regulated system, often within a cap-and-trade framework. |
| Standardization | Verified by independent standards (e.g., Verra, Gold Standard). | Governed by regulatory standards and rules. |
| Compliance & Penalties | No legal penalties for non-participation. | Legal penalties for exceeding emissions limits without proper allowances. |
What are the benefits of voluntary credits?
There are a number of different types of carbon credits, and the benefits of voluntary credits are as follows.
Issuers have flexibility in design and generation
Unlike a government-regulated credit where many restrictions in many places prevent flexible credit design, the voluntary credit has more flexibility in its design and generation through companies, NGOs, and private organizations that are not legally bound.
purchaser can obtain benefits for decarbonizationIn line with decarbonization as a measure to prevent global warming on a global scale, companies are also proactively setting targets for environmental measures such as CO2 reduction in order to increase their own environmental value. However, due to the diversity of a company’s economic activities, it can be difficult to achieve goals through internal efforts alone. Because voluntary credits are provided by private organizations, there are no policy restrictions or legal obligations, and they are very convenient for companies, so demand is expected to continue to grow.
Can offset greenhouse gas emissions that are difficult to reduce
In order to use voluntary credits, each company must make concrete efforts to decarbonize. This is because voluntary credits are only a means of carbon offsetting and are not an essential means of reducing CO2 emissions.
While implementing a decarbonization plan and gradually reducing CO2 emissions, it is recommended to use voluntary credits which enables to offset greenhouse gas emissions that are difficult to reduce due to business activities.
What are the challenges of voluntary credits?
Price uncertainty
As noted above, the price of voluntary credits is determined through bilateral transactions between companies. The downside is that the purchase prices are difficult to predict because market forces operate based on the ever-changing balance of supply and demand, making it difficult for companies to manage their budgets.
Credibility of GHG reduction projects
Voluntary credit is not certified by the United Nations or the government, but is a private sector led system, so special care must be taken to ensure reliability. When purchasing, it is encouraged to choose a reliable GHG reduction project that has been certified by an appropriate certification body, and then conduct thorough the verification.
How can voluntary credits be used effectively?
There are two ways to effectively use voluntary credits in the business activities after purchase.
Voluntary reduction of CO2 emissions in business activities
Voluntary credits are a highly effective way to voluntarily work towards carbon neutrality in business activities.
Voluntary credits can be used to demonstrate to stakeholders such as financial institutions, shareholders and investors that the company’s value can be enhanced. In addition, making such an announcement to business partners can help them take concrete action to reduce CO2 emissions throughout the supply chain in the future.
Promote company’s global warming countermeasures
The voluntary credits can be used to offset the CO2 emissions of its own events, or add value by making carbon-neutral products. In addition, by introducing carbon credits that are highly relevant to the business, you can contribute to the revitalization of local industries and educational activities. In addition to being able to publicize externally that the company is “a company that is committed to decarbonizing management” it is also expected to attract a customer base with high environmental awareness, leading up to improved its image and gaining trust.
What Does It Mean To Be Carbon Negative? Difference Between Carbon Positive and Carbon Neutrality
CONTACT US
Please feel free to contact us at anytime.
We will get back to you as soon as we
can!
Editor
OFFSEL Owned by Erevista Inc, OFFSEL is specializes in Environmental issues, especially in carbon neutrality. We primarily provide the latest information on environmental energy.