What is TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures)?
- CO2-reduction
Table of Contents
What does TCFD stand for?
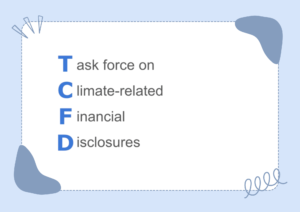
TCFD ( Task force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures) is an internationally organized group dedicated to encourage companies to proactively disclose their efforts to address climate change.
Generally speaking, when we simply refer to TCFD, it’s offered to the recommendations put together by the task force rather than the group itself.
In a nutshell, TCFD recommends to disclose how and to what extent a company is likely to be financially affected by climate change, and what measures are being taken. Investors and financial institutions use this information when deciding whether to invest or provide financing.
In response to the Paris Agreement, which was decided to take steps to reduce greenhouse gasses and raise awareness of environmental issues around the world, one work project was initiated and a corresponding task force was formed. It was TCFD that was established in 2015 by the Financial Stability Board (FSB), an international organization that aims to stabilize the financial system.
After a year and a half of discussions, the TCFD released the TCFD Recommendations (Final Report) in 2017. The TCFD recommendations serve two purposes:
- To encourage companies to disclose climate-related financial information in a consistent, comparable, reliable, clear, and efficient manner
- To encourage investors, etc. to make appropriate investment decisions
In this way, TCFD serves as a basis for both investors and investee companies to address environmental issues. By measuring and visualizing a company’s potential climate risks in a way that financial statements alone cannot, TCFD-compliant disclosure has the advantage of making it easier to gain the trust of investors.
What is the background to the creation of TCFD?
The following three reasons can be highlighted why TCFD was established:
- Climate crisis is worsening.
- The Paris Agreement sets a global climate agenda.
- Financial reporting standards are being reviewed and changed.
Climate crisis
Since the Industrial Revolution, humanity has transitioned into an industrialized society and enjoyed material abundance that continues to this day.
However, this has degraded the natural environment and increased emissions of greenhouse gasses such as CO2. Since then the Earth’s temperature has risen significantly: between 2011 and 2020 alone, the temperature has risen by about 1.59℃ on land and about 0.88℃ over the ocean compared to pre-industrial levels.
Related article:
What is the Greenhouse Gas(GHG)Protocol? Explaining the Definition, Scope 1~3, and Corporate Standard.
Paris Agreement as a global climate agenda
In response to this situation, the Paris Agreement was adopted as a new international framework to reduce greenhouse gas emissions after 2020 onwards.
The Paris Agreement was a global agreement signed by the United States and China, the two largest emitters, as well as by developing countries that were reluctant to take action against global warming.
Financial reporting standards under review and changed
It has been widely recognized that the increased frequency of extreme wether events associated with climate change has become a threat to the stability of the financial system. There are three underlying risks:
- Physical risks: Risks such as property damage from natural disasters such as floods, storms, disruptions in the global supply chain, and resource depletion.
- Liability risks: Risks that arise when parties affected by climate change losses seek compensation from others and attempt to recover those losses.
- Transition risks: Risks arising from the re-evaluation of companies with high greenhouse gas emissions as they transition to a low-carbon economy.
This type of investment approach is known as ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing. Investors and financial institutions have begun to require companies to provide specific ESG-related information including decarbonization targets from the companies they invest in or lend to and have also sought substantial reductions in CO2 emissions from their investment targets to mitigate these risks.
As a result, when financial institutions provide financing to companies based on their climate change mitigation efforts, their commitment to the TCFD recommendations has become one of the evaluation criteria.
Four thematic areas that TCFD recommends

To comply with the TCFD recommendations, each company is encouraged to disclose financial information across four core elements and eleven items. However, it is not always necessary to disclose all of them. What is required for a company is to disclose information necessary for investors and financial institutions to understand the financial impact of climate change and to be able to make decisions based on them.
Governance
“Governance” refers to how an organization deals with climate-related risks and opportunities and how management decisions are made based on them. There are two key aspects to this element:
- Explanation of the board’s oversight mechanism.
- Description of the roles of senior management in assessing and managing climate-related issues.
This information is required as it indicates how the management team and the board of directors consider climate-related issues and the extent to which they are involved.
Strategy
“Strategy” refers to the risks and opportunities associated with climate change in the short, medium, and long term. It also includes how climate change affects a company’s business, tax position, and overall strategy.
Particular emphasis is placed on the specific financial impacts of risks and opportunities and whether robust strategies have been developed. Scenario analysis, as discussed in more detail below, falls under this element.
Risk Management
“Risk management” refers to how companies organize, assess, and manage climate-related risks and opportunities. It includes how climate-related risks and opportunities are identified, assessed, managed, and integrated into the organization’s overall risk management.
Metrics and Targets
“Metrics and targets” focuses on defining clear indicators for assessing climate-related risks and opportunities. “GHG Protocol” is a commonly used indicator for measuring greenhouse gas emissions, but there are no specific rules for TCFD on which indicators to use. In this regard, it is essential to disclose how the criteria was develop for a specific target and then to provide a detail on the company’s current and past efforts.
Sources: https://assets.bbhub.io/company/sites/60/2020/10/FINAL-2017-TCFD-Report-11052018.pdf
What is scenario analysis in TCFD?
Scenario analysis is an effective way for companies to strategically address the challenges posed by long-term and uncertain climate change issues. It involves the creation of different scenarios based on climate change and associated risks such as deteriorating business conditions.The goal is to anticipate these risks and develop appropriate strategies.
Scenario analysis is primarily conducted through the following steps:
- Define the scope and time frame of the analysis.
- Assess the significance of risks.
- Define a set of scenarios.
- Evaluate the business impacts of these scenarios.
- Define response strategies.
- Describe and communicate the information.
Scenario analysis requires significant effort. It often requires collaboration with different departments within the organization as it is not a work that can be done in a single department. Furthermore, it requires a tremendous amount of effort especially in high-emitting industries.where climate change risks are huge. In addition, it is expected that various risks related to climate change will emerge in the future.
On the other hand, however, TCFD and other types of non-financial disclosures not only identify risks but in some cases may also present opportunities.
In this regard, companies may find it useful to conduct scenario analysis that considers different strategies. TCFD-compliant disclosures not only provide opportunities and benefits to companies, but also serve as valuable information for investors. Therefore, it is important to understand its significance and to adopt it and address it early as a sustainable management practice of a company.
You May Also Interested In:
Basic Information About SBT (Science Based Targets) Initiative: What’s the Difference Between RE100?
A guide of Carbon Neutrality – What is the Difference between Net Zero and Decarbonization?
CONTACT US
Please feel free to contact us at anytime.
We will get back to you as soon as we
can!
Editor
OFFSEL Owned by Erevista Inc, OFFSEL is specializes in Environmental issues, especially in carbon neutrality. We primarily provide the latest information on environmental energy.