Summery of the Paris Agreement
- CO2-reduction
Table of Contents
What is the Paris Agreement?
The Paris Agreement that indicates a framework for reduction of greenhouse gasses.
It is also known as COP21 and the purpose of it was to upgrade the Kyoto Protocol to improve climate change situations. The latest GHG emissions situation in each country, which has changed in less than 20 years since the Kyoto Protocol, is considered.
Background of the Paris Agreement
To understand better about the Paris Agreement, let’s review its history1992: UNFCCC adopted
Scientific innovations from the 1970s to 1980s caused climate change and global warming. The situation was as serious as requiring global efforts, and the fact was mentioned in a report by the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) in 1988.
In 1992, the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development was held and the Earth Summit framework that indicates the reduction of greenhouse gas emission was agreed. Two years later, in March 1994, the UNFCCC was adopted.
The most important objective of that treaty was the stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations. Although 197 countries have signed the treaty, developed countries (Annex I Parties) were required to take measures and report to achieve clearer goals, as well as provide financial assistance to developing countries.
1997: The Kyoto Protocol Agreement
Though UNFCCC from 1992 was an innovative idea, it had no compelling force.Therefore, it was necessary to set more legally binding numerical targets, mainly for developed countries with large emissions.
In 1997, the Kyoto Protocol was adopted for developed countries to set and implement more specific targets for climate change.The Kyoto Protocol sets greenhouse gas reduction targets for developed countries to achieve between 2008 and 2012. Specifically, a reduction of at least 5.2% is required from the 1990s reduction standard year, with Japan’s reduction target being 6%, the US 7%, and the EU 8%.
2015: Paris Agreement concluded

The Kyoto Protocol was indeed legally binding, with provisions for penalties. However, since greenhouse gas emissions increased from economic growth between 1990 and 2000, the Kyoto Protocol only worked as a deterrent so it failed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions practically.
It required new standards for developing countries including China that had not signed the Kyoto Protocol.
Therefore, COP21 was held in 2015 and the Paris Agreement was adopted. It became effective in November 2016 and Japan signed it on the 8th of November.
America and China Signed
In the Paris Agreement, America and China participated though America disapproved and withdrew from the Kyoto Protocol and China was excluded under the Kyoto Protocol.
Here are the reasons why 2 largest greenhouse gas emitters participate in the Paris Agreement.
- To obtain an international initiative
- To set achievable goals for a sustainable future
- To fight climate change
America and China are the 2 largest countries as greenhouse gas emitters as well as economies GDP. Since they are influential countries, it was understandable that the Paris Agreement that set goals for both developed and developing countries was ratified.
In fact, America’s actions for the Paris Agreement changed several times as follows.
- 2015 – Adopted
- 2016 – Became effective
- 2017 – Announcement of withdrawal
- 2020 – Officially withdrawn
- 2021 – Signed it again
When the Paris Agreement was adopted in 2015, president Obama had a great interest in climate change and that was the reason why America participated. Then in 2017, since president Trump criticized the Paris Agreement, America officially withdrew from the agreement in 2020. The current resident Biden signed the Paris Agreement in 2021.
In China, serious air pollution was becoming a social problem despite rapid economic development. It was crucial for Japan to obtain the leadership of the Paris Agreement to prioritize environmental issues and gain public support.
Aiming for net-zero economy
Parties that signed the Paris Agreement have missions to reduce greenhouse gasses as well as economic growth to achieve the long-term goals since a decarbonized society requires renewable energy replaced from fossil and parties need innovation and investment.
In fact, there are business benefits to combating climate change. For example, since renewable power generation such as solar has been more reasonable for the last 10 years, renewable energy is a lower cost option than fossil fuels and businesses can turn profits.. In the future, it is predicted that the renewable energy business will encourage investors to make ESG investments, expand the market scale toward the major mission of energy replacement, and promote economic growth.
Key aspects of the Paris Agreement
Here are contents that are included in the Paris Agreement.
The central aim of the Paris Agreement
There are 2 different goals for the Paris Agreement as below.
The temperature rise needs to be less than 2℃, and try to less than 1.5℃ and the industrial revolution is utilized for comparison.
Since this is only a long-term goal, each country must develop and submit its own reduction targets. Specifically, major countries have set the following 2030 goals.
※Source: The New Climate Institute
From 2013 levels, Japan aims for 46% of reduction. From 2005 levels, America aims for 50-52%, Brazil targets 40-45%, and per GDP, China indicates at least 65% and India has 45%.
South Korea targets 40% from 2018 levels.
The targets will be updated to ambitious climate action every 5 years. Japan originally set a target of 26% reduction (from 2013 levels) then it has changed to 46% in 2021.
Countries signed with Paris Agreement
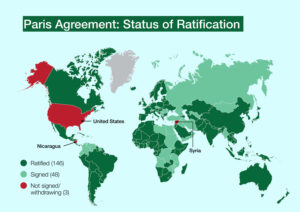
196 parties participated in the Paris Agreement. List some countries.
Source:JCCCA
- uk
- America
- EU countries
- Australia
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- China
- Indonesia
- Canada
- Saudi Arabia
- Türkiye
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Russia
The Paris Agreement became effective in 2019 and until then America, Syria, and Nicaragua were not in the list.
However, America returned in 2021, and Syria and Nicaragua also ratified the agreement of the Paris Agreement in 2017.
Contents of the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement mainly established the following points as rules for signatory countries.
- All Parties Submit Reduction Targets (NDCs)
- All signatories must update and submit their NDCs once every five years.
- All signatories submit progress on emissions reductions every two years
- Developed countries actively provide financial aid to developing countries
- Utilize carbon credit systems etc. to help each country achieve its goals
The Paris Agreement required all signatories to set and submit clear reduction targets (NDCs) and take concrete steps to achieve these targets. Furthermore, the targets must be reviewed and resubmitted every five years.
The goals are required to be reviewed and resubmitted every 5 years. There are same rules for developed and developing countries to achieve the goals, however, developed countries are obligated to support developing countries financially for improving greenhouse gas reduction.
[*] The Paris Agreement and the Kyoto Protocol differences
Here are different rules between The Paris Agreement and the Kyoto Protocol:
Only developed countries can sign and they have a scheme to achieve the targets in the Kyoto Protocol.
It became mandatory to formulate and submit reduction targets instead of achieving them.
The parties for the Kyoto Protocol are only for developed countries, however, the Paris Agreement expanded to all countries including developing countries. This will enable developing countries to implement advanced measures to reduce greenhouse gases while receiving active support from developed countries.
Although the Paris Agreement clarified long-term goals regarding temperatures, parties adopted a “bottom-up” idea that each party can set goals. It helps us to plan and promote the most reasonable ways suited to each party.
The content of what is mandatory has also changed. The Kyoto Protocol required to “achieve” the goals within the set terms, however, parties are obligated to “submit” and “upgrade” the targets every 5 years in the Paris Agreement.It is necessary to review and update goals.
※Source: Parliament of Australia
Even though the Paris Agreement has less obligations for the parties than the Kyoto Protocol, it has more reasonable and fair rules for all parties.The participation of countries with large emitters, such as America and China, is also a reason for developing countries receiving aid to follow suit.
Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions for businesses
To reduce greenhouse gas emissions, businesses can try 3 ways.
Introduce renewable energy
If businesses introduce renewable energy, they can reduce greenhouse gas emissions effectively and there are different types of models for intruding the system as below.
– Install own renewable energy facility for energy self-sufficient
– Purchase renewable energy from energy suppliers
-Energy suppliers install a power facility and the company purchase the generated electricity (PPA)
When businesses install solar power facilities and generate renewable energy in the precinct, it reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
However, setting up a power facility requires budgets. If businesses seek ways to save costs, there are “PPA” models that energy suppliers install, or the renewable energy plan provided by a contracted energy supplier. It is essential for businesses to choose one of the ways.
In the PPA model, the installation costs are borne by the power company and they only need to rent out their own facilities and land, which can significantly reduce costs.
If businesses switch to a “renewable energy electricity plan”, they can introduce renewable energy immediately, however, this way requires a higher amount of running expenses.
Introduction of energy-saving equipment
Companies can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by introducing various energy-saving equipment. Examples of specific implementations include the following.
-Change factory boiler facilities to ones with higher energy consumption efficiency
-Change all in-house air conditioners to models with lower power consumption
-Change all in-house lighting equipment to LED
It is recommended to talk to experts when we seek the improvement of energy-saving as they have ideas of more effective ways.
Carbon offsetting
If companies cannot achieve their reduction targets through their own efforts, they can do so by compensating by purchasing environmental value (carbon offsetting).
When they purchase credits or certificates that issued by other businesses are regarded as a reduction.
For the achievement of the Paris Agreement, the world is aiming to prevent climate change and decarbonization that the Kyoto Protocol failed.
By conducting reduction activities in accordance with clear targets and guidelines set by the company and publishing the results, companies can establish their social standing and attract active investment from investors.
CONTACT US
Please feel free to contact us at anytime.
We will get back to you as soon as we
can!
Editor
OFFSEL Owned by Erevista Inc, OFFSEL is specializes in Environmental issues, especially in carbon neutrality. We primarily provide the latest information on environmental energy.