What Are The Non-Renewable Resources? Definition, Examples, Pros And Cons
- CO2-reduction
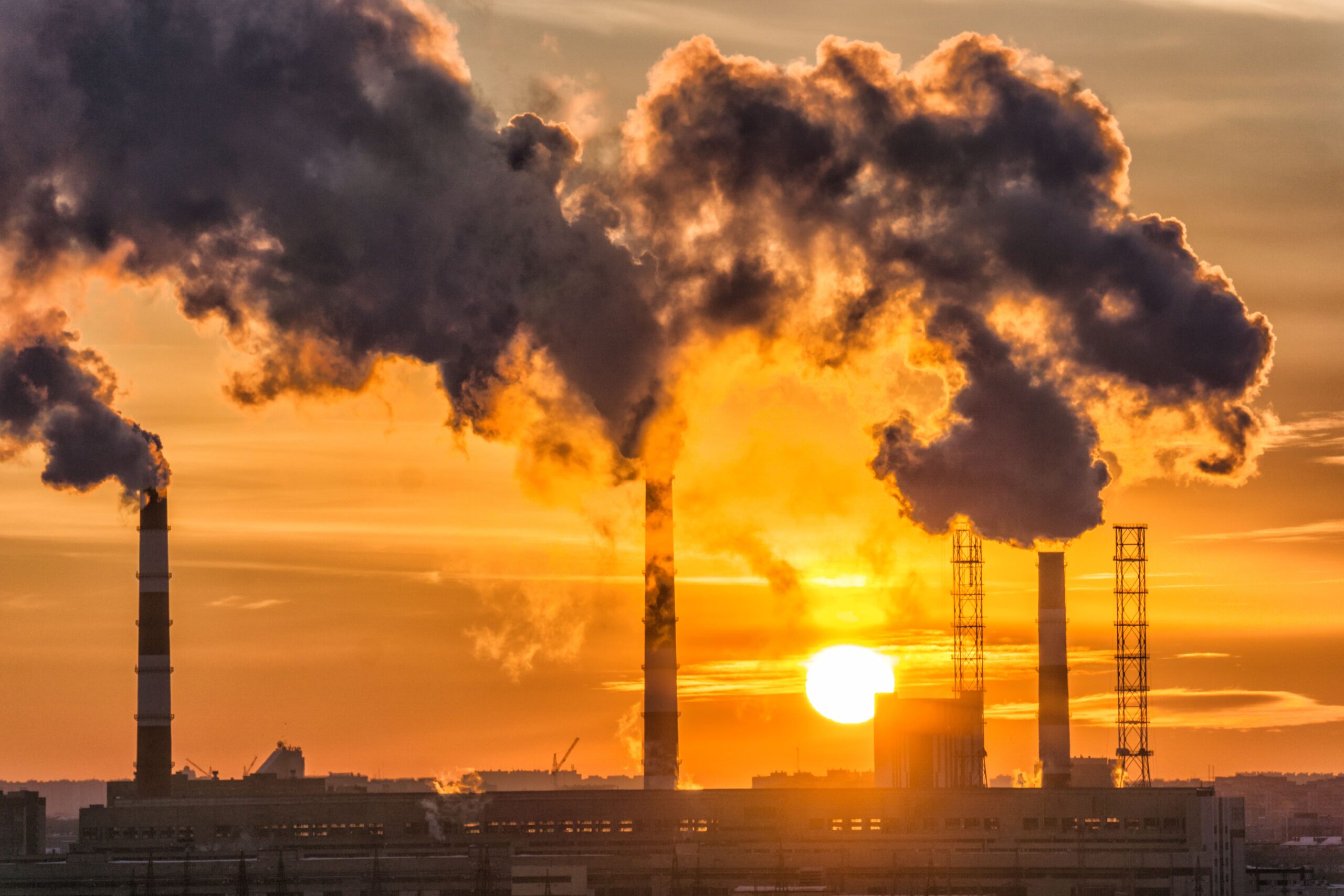

Non-renewable resources are materials found on Earth that do not replenish themselves at a rate that allows for sustainable extraction and use. They are pivotal to modern society, powering industries, homes, and transportation systems. Understanding their advantages and disadvantages, alongside a clear comparison with renewable resources, is critical for a balanced view of our current energy landscape.
Table of Contents
Examples of non-renewable energy
Coal
Coal, a black or brownish sedimentary rock, is formed from decomposed plant matter under high pressure and heat over millions of years. It’s primarily composed of carbon, with traces of hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal mining, both surface and underground, is the primary method of extraction. It’s mainly used for electricity generation through combustion and is also a critical raw material in the steel-making process. However, coal burning is one of the largest sources of carbon dioxide emissions, significantly contributing to global warming and air pollution.
Oil
Oil, also known as petroleum, is a liquid fossil fuel formed from ancient marine organisms. Extraction involves drilling into the earth, often offshore, to tap into oil reservoirs. It’s a highly versatile resource, refined into various fuels like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel, and used as a base for countless chemical products, including plastics and pharmaceuticals. The oil industry is a major economic driver but faces criticism for oil spills and its substantial contribution to greenhouse gas emissions.
Natural gas
Natural Gas is a cleaner-burning fossil fuel, primarily composed of methane. It’s found in underground reservoirs, often alongside oil, and is extracted through drilling. Natural gas is used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation and increasingly as a cleaner alternative to other fossil fuels in power plants. It’s also a key raw material in the production of chemicals and fertilizers. While it emits fewer pollutants than coal or oil, methane leaks during extraction and transport pose significant environmental risks.
Nuclear energy
Nuclear energy, derived from the fission of radioactive elements like uranium, provides a high energy output with minimal greenhouse gas emissions during operation. Nuclear power plants generate electricity through controlled nuclear reactions. The major concerns with nuclear energy are the risks of nuclear accidents, as seen in Chernobyl and Fukushima, and the challenge of safely managing nuclear waste, which remains radioactive for thousands of years. Despite these issues, nuclear energy is considered a significant non-renewable alternative to fossil fuels in the fight against climate change.
Advantages of non-renewable resources
High Energy Efficiency
Non-renewable resources, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are renowned for their high energy density. This implies that they can deliver a large amount of energy from a relatively small volume. For instance, coal, when burned, releases a significant amount of heat energy, making it a preferred choice for power generation in many parts of the world. Similarly, oil and natural gas have been pivotal in driving the mechanization and mobility that define modern civilization. Their high calorific value means that vehicles, power plants, and industries can achieve a high output of energy, supporting extensive transportation networks and industrial operations with relatively compact fuel quantities. This characteristic is particularly crucial in sectors where energy density and the ability to release energy quickly are vital, such as in aviation, shipping, and heavy manufacturing.
Infrastructure and Technological Advancement
Over the years, a comprehensive global infrastructure has been developed for the extraction, refinement, and distribution of non-renewable resources. This network includes everything from oil rigs and coal mines to pipelines and refineries, all supported by a vast logistics and transportation framework. The technological strides made in these areas have not only streamlined these processes but have also introduced significant efficiencies and safety improvements. For example, advancements in drilling technology have made it possible to access oil and gas reserves that were previously unreachable, significantly expanding the supply of these crucial resources. Moreover, improvements in refining processes have maximized the yield of valuable products from crude oil, enhancing the overall efficiency of the oil industry. This mature infrastructure facilitates the continuous and reliable supply of energy, essential for the functioning of the global economy.
Economic Impact
The economic implications of non-renewable resources extend far beyond their immediate contribution to energy production. The exploration, extraction, refining, and distribution of these resources are cornerstones of the global economy, creating a wide spectrum of jobs across various sectors. From geologists and engineers in the extraction process to workers in power plants and refineries, the industry supports millions of livelihoods worldwide. Furthermore, the revenues generated from non-renewable resources play a pivotal role in the national budgets of resource-rich countries, funding public services and infrastructure development. The economic benefits also trickle down to ancillary industries, including manufacturing, transportation, and services, which rely on the energy supplied by non-renewable sources or are directly involved in their supply chain. This complex web of economic activities underscores the critical role non-renewable resources play in sustaining economic growth and development across the globe.
Disadvantages of non-renewable resources
By implementing these strategies, we can make significant progress in reducing our dependence on non-renewable energy sources and move towards a more sustainable and cleaner energy future.
CONTACT US
Please feel free to contact us at anytime.
We will get back to you as soon as we
can!
Editor
OFFSEL Owned by Erevista Inc, OFFSEL is specializes in Environmental issues, especially in carbon neutrality. We primarily provide the latest information on environmental energy.