What is the Carbon Neutrality Coalition (CNC) and how they are made?
- CO2-reduction

Table of Contents
What is the Carbon Neutrality Coalition?
 Cited from: Carbon Neutrality Coalition
Cited from: Carbon Neutrality Coalition
The Carbon Neutrality Coalition is an international initiative that brings together countries committed to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. It represents a unified response to the urgent challenges posed by climate change, aiming to transition the world towards a sustainable, low-carbon future.
History of the CNC
In response to the Paris Agreement, the Carbon Neutrality Coalition was formally established in 2017 during the United Nations General Assembly.
The founding members of the coalition, including small island nations and some European countries, were among the first to acknowledge the need for a zero-carbon future. Their vision was clear: to lead by example and encourage other nations to commit to ambitious carbon neutrality targets.
Countries that joined the commitment agreed to the followings:
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Implementing strategies to significantly cut emissions by 2050.
- Enhancing Sustainable Practices: Promoting renewable energy, sustainable transportation, and energy efficiency.
Three thnigs CNC aims for
List of the countries
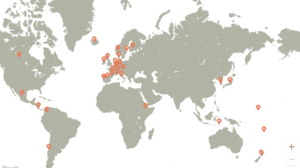 Cited from CNC
Cited from CNC
Countries from across the globe have joined the coalition, each bringing unique commitments and strategies to the table. These nations include:
- European Union (EU): Comprising 27 member states, the EU has been a frontrunner in climate policy, setting ambitious targets for reducing emissions and transitioning to renewable energy.
- United States: Rejoining global climate efforts, the US has pledged to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, emphasizing renewable energy and green technology.
- Canada: Committed to net-zero emissions by 2050, Canada is focusing on clean energy, carbon pricing, and sustainable industries.
- Japan: Japan aims for carbon neutrality by 2050, with plans to revamp energy infrastructure and invest heavily in green technology.
- United Kingdom: The UK has legislated for net-zero emissions by 2050 and is advancing in areas like offshore wind energy and green finance.
- New Zealand: Targeting carbon neutrality by 2050, New Zealand is focusing on renewable energy and sustainable agriculture.
- France: With a goal for carbon neutrality by 2050, France is investing in nuclear and renewable energy and promoting sustainable transport.
- Germany: Germany, aiming for carbon neutrality by 2045, is phasing out coal, boosting renewable energy, and focusing on energy efficiency.
These countries, among others, represent a diverse and powerful coalition, each contributing to a shared vision for a carbon-neutral world.
733 cities, 31 regions, 3,067 businesses, 173 of the biggest investors, and 622 Higher Education Institutions have also committed to reach carbon neutrality by 2050 under the Race to Zero campaign.
The journey towards carbon neutrality is fraught with challenges, from technological barriers to political and economic constraints. The coalition, through its collective wisdom and resources, is continuously working to overcome these hurdles.
CONTACT US
Please feel free to contact us at anytime.
We will get back to you as soon as we
can!
Editor
OFFSEL Owned by Erevista Inc, OFFSEL is specializes in Environmental issues, especially in carbon neutrality. We primarily provide the latest information on environmental energy.